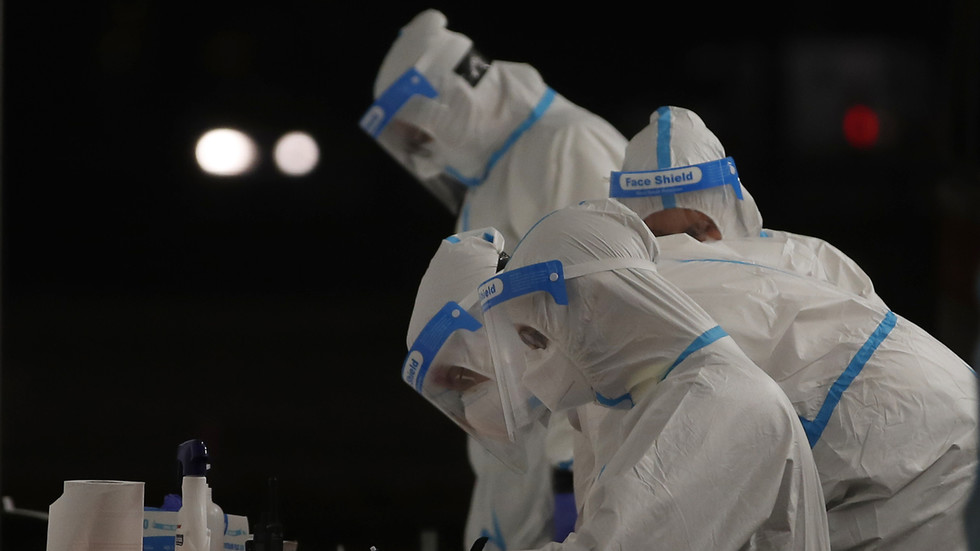
New research from India suggests that a deficiency of the protein Alpha-anti-trypsin (AAT) in populations across Europe and North America may have contributed to the comparatively rapid spread of Covid-19 when compared with Asia.
Published in the journal Infection, Genetics and Evolution, the new study examines the role played by a lung-protecting protein in the spread of the pandemic in the West compared with Asia.
Continue reading https://on.rt.com/b1gx